What are Heat Maps?
A Heat Map (or Heatmap) is a graphical 2-dimensional format representation of data where values are depicted by color.
Heat maps make it easy to visualize complex data and understand it at a glance.
In other words, Heatmaps is about replacing numbers with colors because the human brain understands visuals better than numbers, text, or any written data.
In Software Testing color give visual cues about how data are clustered or varies over the testing process.
Heatmaps can describe the density or intensity of variables, visualize patterns, variance, and even anomalies. Heatmaps show relationships between variables.
Color variation gives visual cues to the readers about the magnitude of numeric values.
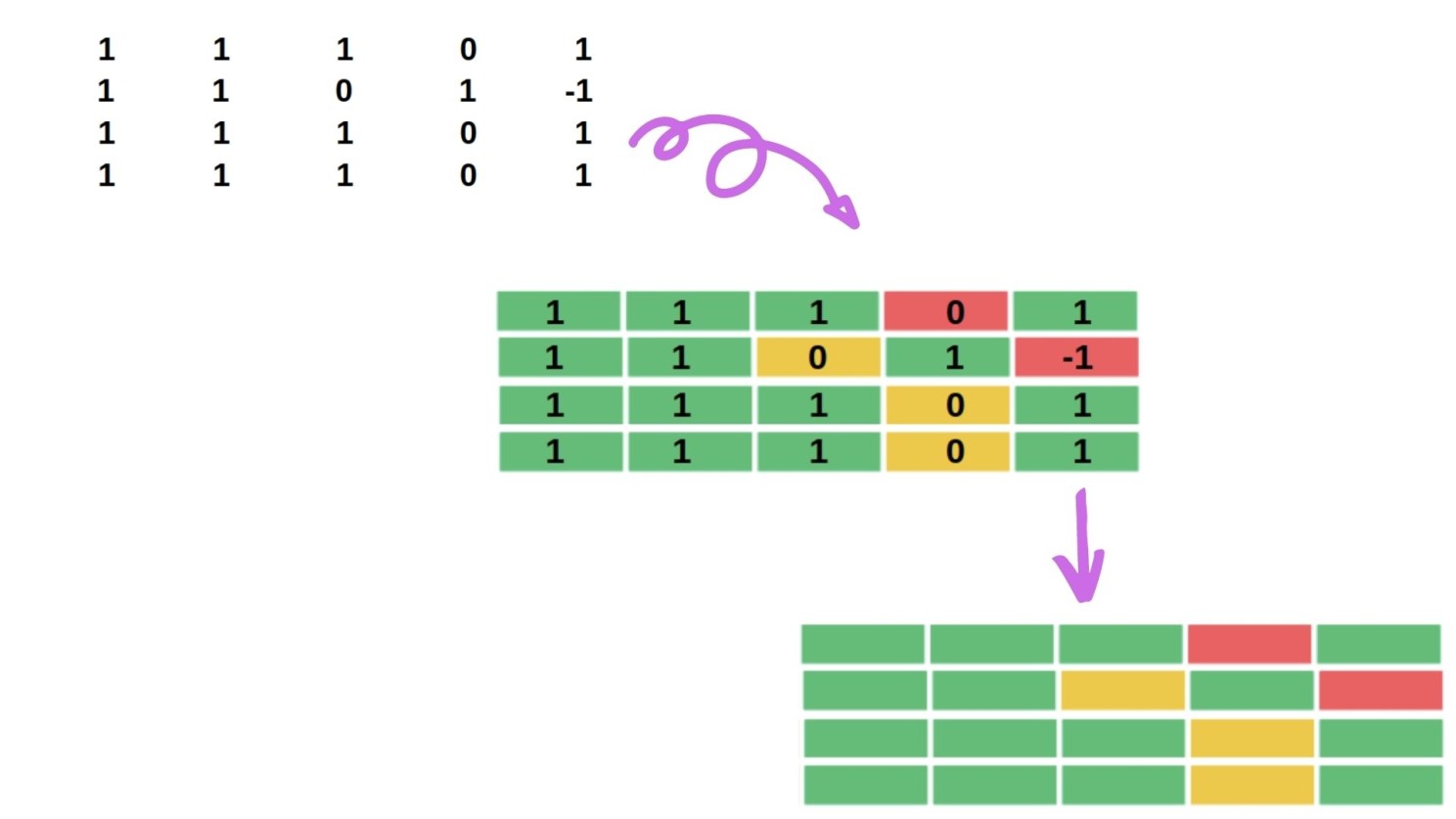
These Heatmaps are data-driven “paint by numbers” canvas overlaid on top of an image. The cells with higher values than other cells are given a hot color, while cells with lower values are assigned a cold color.
6 interesting facts about Heatmaps:
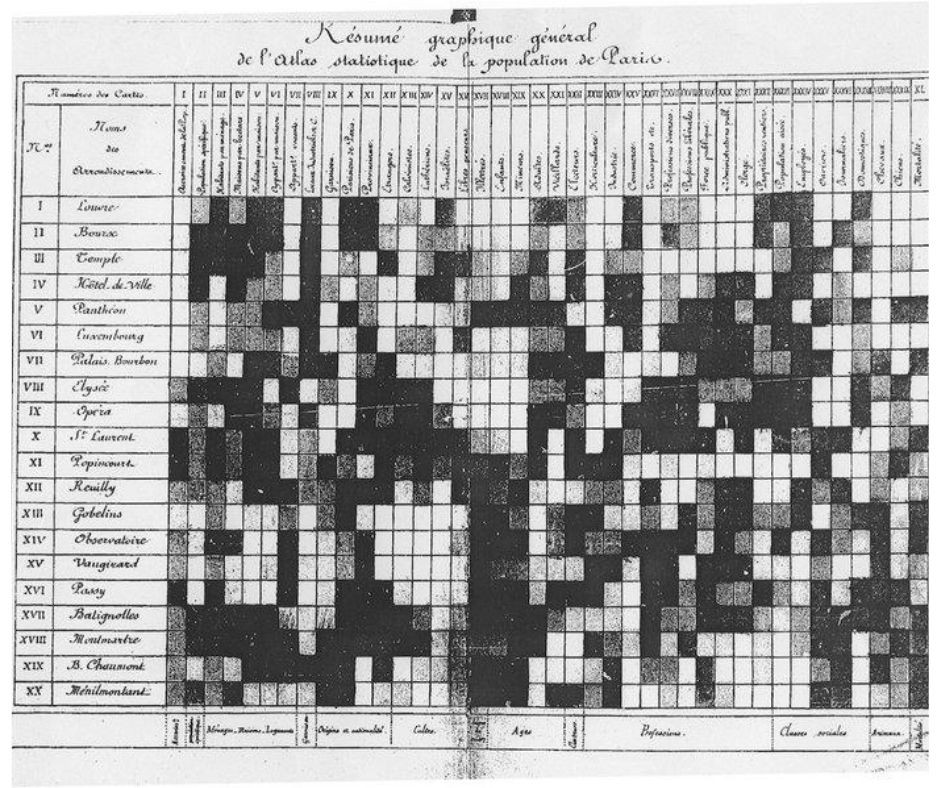
- The practice we now call heat maps is thought to have originated in the 19th century, where manual grey-scale shading was used to depict data patterns in matrices and tables. See, original Heat Map of the 19th century, where manual grey-scale shading was used to depict data patterns in matrices and tables.
- Spectrum rainbow colors are best perceived, so nowadays we can see colored models. Note, good color schemes help you see structure in numeric data. Lighter colors correspond to smaller amounts and darker shades to larger values, or vice versa.
- The term “Heatmap” was first trademarked in the early 1990s, when software designer Cormac Kinney created a tool to graphically display real-time financial market information.
- In the Software Testing, the first mention was for prediction of the reliability of large software products, the technique was evaluated on Microsoft Vista and Eclipse.
- Heatmaps are the most commonly used for studying genomes to represent the level of expression of many genes.
- Also, Heatmaps are popular in marketing researches and sales. In testing as a website UI/UX testing, A/B testing, Performance testing.
What is a website heat map?
Website heatmaps visualize the most popular (hot) and unpopular (cold) elements of a webpage using colors on a scale from red to blue.
Displays user behavior, heatmaps facilitate data analysis and give an at-a-glance understanding of how people interact with an individual website page — what they click on, scroll through, or ignore—which helps identify trends and optimize for further engagement.
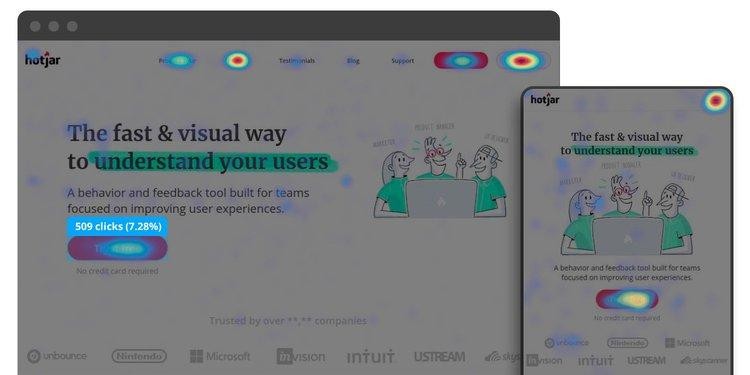
So, website heatmaps are popular to carry out UX/UI testing and A/B testing, Performance testing. Visualize users’ preferred browsing and shopping behavior etc.
The benefits of using heat maps:
- Visualization makes it easy to spot strong dependencies. Yeah, it is essentially a kind of a Real-Time report.
- Shows patterns and data dependencies.
- Display changes over time.
- Heatmaps help locate hidden errors, understand the problematic parts of the product under development.
- Based on these, QA Engineers uses Heatmaps for prioritizing test effort with the early warning.
- Stakeholders for making the right decisions.
- Businesses can improve systems by identifying, monitoring and correcting anomalies.
🗒 Summary
Heatmaps represent data in an easy-to-understand manner to communicate to team members or clients. Thus visualizing methods like HeatMaps have become popular.
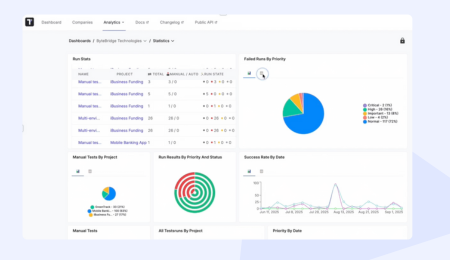
Testomat.io Test Management System provides Test results Heatmaps by test suite on Test Reports. Heatmaps shouldn’t be used apart. Good practice correlate them to analytics and the context of your research, what we successfully developed into our Test Management tool as well. Rich Analytics is available in Professional, Enterprise and in Free Trial plans 😉
Analytics widgets include:
- Flaky Tests
- Slowest Tests
- Never Run
- Tests Ever
- Failing Tests
…and many more.